How to Set Up a Family Office in Malaysia: Comprehensive 2026 Guide

Executive Summary: Why Malaysia Matters for Families in 2026
Setting up a family office is no longer just a tax decision. For ultra-high-net-worth families, it is a long-term operating strategy for governance, investment control, and intergenerational continuity.
In 2026, Malaysia has emerged as a credible family office jurisdiction with the introduction of a structured Single Family Office (SFO) framework under the Forest City Special Financial Zone (SFZ). The framework is designed to attract single-family wealth platforms by combining targeted tax incentives with clear economic substance requirements and a regulated annual certification process.
This guide explains how to set up a family office in Malaysia using a professional approach. It outlines the operating model, compliance pathway, implementation sequence, and key strategic decisions families should evaluate.
Important Notice
This article is provided for general information and educational purposes only. It does not constitute legal, tax, investment, or regulatory advice. Family office frameworks and incentives may change, and approvals are subject to regulatory discretion. Readers should obtain professional advice before implementing any structure described here.
What It Means to Set Up a Family Office — and Why Malaysia
To set up a family office is to establish a dedicated platform for managing a family’s investments, governance, reporting, and long-term wealth strategy. Rather than acting as a single investment vehicle, a family office functions as an operating system that formalises decision-making, risk management, and succession across generations.
When choosing where to set up a family office, families typically prioritise regulatory clarity, tax efficiency, cross-border flexibility, operating cost, and access to professional expertise. Malaysia’s framework in 2026 addresses these factors through a structured Single Family Office regime under the Forest City Special Financial Zone.
Positioned near Singapore, Forest City SFZ offers regional connectivity alongside a competitive operating base. Malaysia’s common-law system, established financial services ecosystem, and substance-based requirements make it a practical jurisdiction for families seeking both structure and flexibility.
How to Set Up a Family Office in Malaysia Under the SFO Framework
Malaysia’s SFO framework is anchored to the concept of a single-family platform with defined corporate entities, a regulated certification process, and ongoing annual compliance. At a high level, families create a Malaysian investment vehicle to hold assets, supported by a management entity that provides investment and operational services.
The framework is designed to ensure the family office is not merely a “paper structure.” Instead, it must demonstrate substance in Malaysia—such as local staff, a physical office, and operational spending—while meeting portfolio conditions for local and promoted investments.
Framework Snapshot: A Visual Guide to Set Up a Family Office
The visual below can be used as an internal briefing reference for family principals and advisers. It summarises the structural logic and the key compliance pillars for setting up a family office under the Forest City SFZ approach.
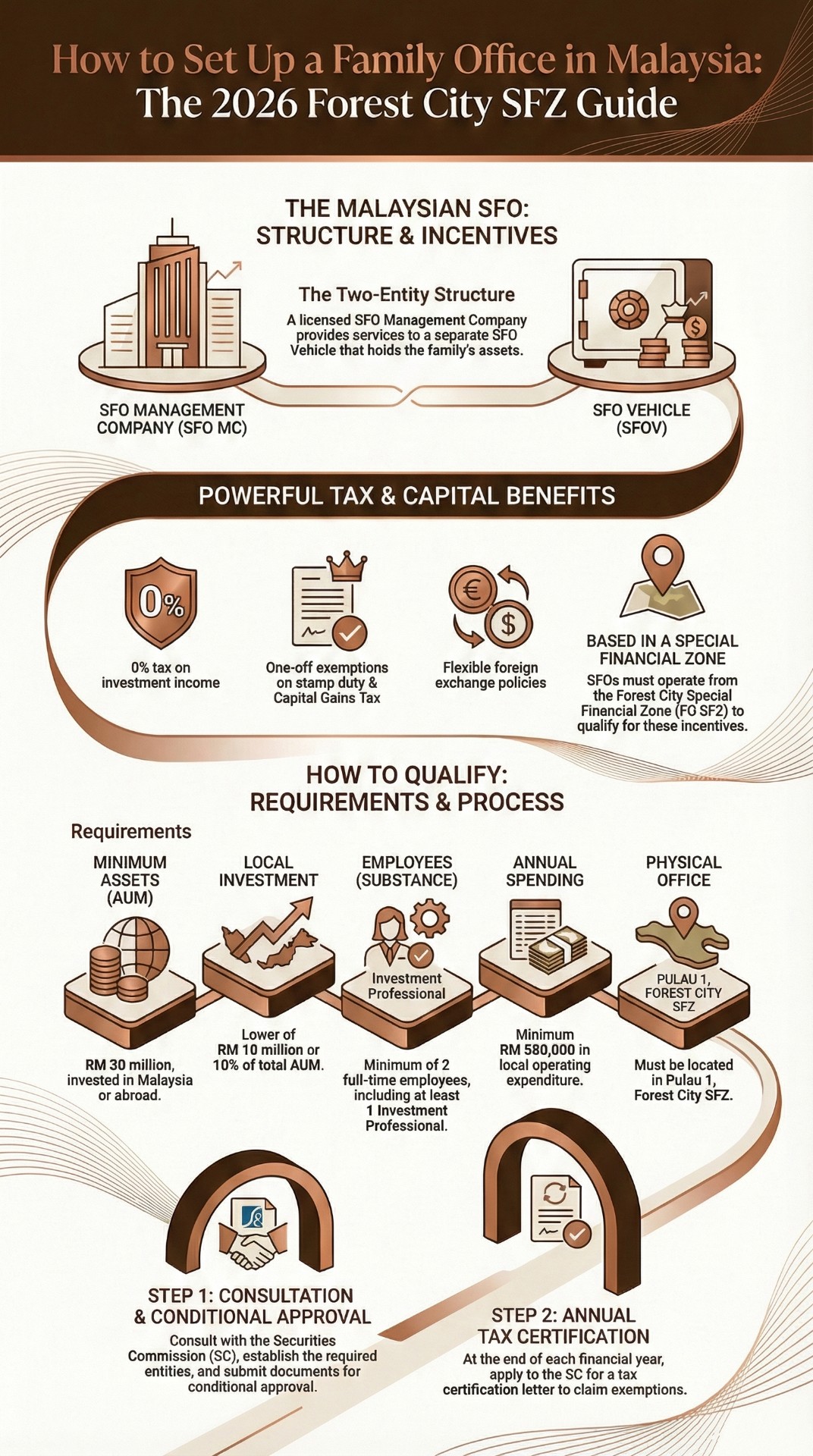
Required Structure to Set Up a Family Office: SFOV and SFO Management Company
To set up a family office within Malaysia’s SFO scheme, the commonly adopted model uses two entities: the Single Family Office Vehicle (SFOV) and the Single Family Office Management Company (SFO MC). This is a familiar concept globally: one entity holds the assets, while another entity provides management services.
The SFOV is the investment holding vehicle. It is established to hold the family’s assets and investments, and it is the entity intended to benefit from the incentive treatment when conditions are met and certified. The SFO MC is the operational management arm. It provides services to the SFOV such as investment management, reporting, governance support, due diligence, and administrative coordination.
A common misunderstanding is that this is a “tax-only” structure. In a best-practice setup, families treat the SFO MC as the institutional engine of the family office: it is where decision-making discipline lives, where reporting is standardised, and where governance mechanisms are implemented. Families that treat SFO MC as a minimal placeholder often face weak controls, higher operational risk, and lower long-term sustainability.
Key Requirements to Set Up a Family Office in Malaysia
Malaysia’s approach is built around a substance-first principle. The policy intent is straightforward: families may enjoy incentives, but only if the family office establishes real operations in Malaysia. This typically includes maintaining minimum AUM thresholds, meeting local/promoted investment expectations, employing qualified personnel, maintaining a physical presence, and incurring meaningful local operating expenditure.
Instead of treating requirements as a checklist, the better approach is to view them as a design constraint for the operating model. For example, staffing thresholds influence the governance design (who makes decisions, who documents them, who signs-off), while local expenditure expectations influence whether to build certain capabilities internally or outsource them to trusted providers.
Practical tip: A credible family office implementation plan usually includes a 12–18 month operating roadmap that aligns staffing, office setup, investment execution, internal controls, and audit readiness, rather than rushing immediately into asset transfers.
Local and Promoted Investments When You Set Up a Family Office
A core feature of the framework is the expectation that the family office participates in local capital development. In practice, this means maintaining local or promoted investments as part of the overall AUM, depending on the applicable threshold and certification period. The promoted investment concept is strategic: it aims to channel family capital toward areas aligned with national development priorities, such as venture investment and sustainability-linked instruments.
The promoted investment “multiplier” concept is especially relevant for families who want to meet the requirement efficiently. In principle, qualifying promoted investments may receive a higher recognition value toward meeting local investment expectations, subject to eligibility and regulator guidance. This creates a practical pathway for families who prefer to invest in higher-growth segments while still meeting policy outcomes.
Good operating practice: Families should document the investment classification decision, the rationale for whether an asset qualifies as local or promoted, and maintain supporting documentation for audit and annual certification purposes.
Key Steps to Set Up a Family Office: The Two-Step Certification Path
From an execution standpoint, families should treat the process as a two-stage journey: (1) initial setup and conditional approval, followed by (2) annual certification discipline. This differs from many jurisdictions where a single approval is sufficient.
Step 1: Establish the Structure and Seek Conditional Approval
The first phase focuses on building the structure and demonstrating readiness: the corporate setup, ownership mapping (to validate “single family” status), operating plan, staffing plan, office readiness, and initial AUM evidence. The goal is to present a coherent and implementable plan rather than an aspirational deck.
Step 2: Run the Family Office as an Institution and Obtain Annual Certification
The second phase is where mature family offices differentiate themselves. Families should implement controls, reporting, meeting cadence (e.g., investment committee), and audit readiness. Annual certification is not a formality—families must demonstrate they are operating within the requirements, and the evidence should be consistent with financial statements, payroll records, office agreements, and investment records.
Consulting-grade implementation insight: The fastest way to reduce compliance risk is to design audit-ready processes from day one (not in month 11). Documentation discipline is usually the difference between smooth certification and stressful remediation.
Governance and Operating Model After You Set Up a Family Office
World-class family offices are built around governance clarity. This means defining who can approve investments, how conflicts are handled, what risk limits exist, and how succession transition is operationalised. A family office that only optimises for tax may look attractive on paper, but it becomes fragile when family complexity increases.
At minimum, families should consider an investment committee structure, a documented investment policy statement (IPS), periodic reporting formats, a compliance calendar, and a protocol for onboarding next-generation members. The operating model should also define what stays in-house versus outsourced (legal, tax, fund admin, accounting, audit, portfolio analytics, trustee coordination, and so on).
FAQ: How to Set Up a Family Office in Malaysia
How much wealth do I need to set up a family office in Malaysia?
For an SFO-style family office platform, families should plan around the prevailing AUM thresholds and certification requirements. In practice, families often begin planning when they have a sizeable investable portfolio and want institutional governance, even before formal application. Always confirm the latest qualifying criteria before implementation.
How long does it take to set up a family office?
A high-quality setup typically takes a few months for structure, documentation, and readiness, followed by ongoing implementation of staffing, operations, investment execution, and annual certification discipline. The timeline depends on asset complexity, cross-border considerations, and how prepared the family is with governance decisions.
Can a family office invest outside Malaysia?
Yes, a family office can maintain a globally diversified portfolio. The key is to manage any local or promoted investment expectations and ensure documentation and reporting standards are consistent with annual certification requirements.
Is a family office only about tax incentives?
No. The strongest family offices are built for governance, decision discipline, and generational continuity. Tax incentives may improve efficiency, but the long-term value is created through institutional control and clarity.
What are common mistakes when families set up a family office?
Common issues include underinvesting in governance, treating compliance as an afterthought, moving assets too early without readiness, and failing to document investment classification and approvals. These gaps often appear during audit and annual certification cycles.
Do I need a partner or adviser to set up a family office?
Many families choose to work with experienced advisers because the setup is multi-disciplinary: corporate structuring, tax planning, governance design, regulatory coordination, asset transfers, and ongoing compliance. Good advisory support reduces execution risk.
Set Up Family Office Outside Malaysia
Many families adopt a multi-jurisdiction approach rather than relying on a single location. The right structure depends on asset location, family residency, banking relationships, and governance objectives. When considering where to set up a family office outside Malaysia — such as Singapore, Hong Kong, or the UAE — the structure should operate as one coherent system, not a collection of disconnected entities.
Timeless International Family Office supports families with jurisdiction comparison, cross-border structuring, governance design, and implementation planning. Whether Malaysia serves as the primary hub or a strategic component within a broader structure, the focus remains long-term control, compliance resilience, and generational continuity.
For a personalised roadmap, request a complimentary consultation with Timeless International Family Office.
References
Outbound references are provided for verification and further reading. For the latest requirements, always refer to official publications.
- Securities Commission Malaysia – Single Family Office (SFO) Tax Incentive page: SC SFO Tax Incentive
- Securities Commission Malaysia – SFO scheme PDF summary (download): SC SFO Summary PDF
- PwC Malaysia – Setting up Single Family Office in Malaysia (download): PwC SFO PDF
- Skrine – Tax incentives for Forest City SFZ (legal commentary, includes gazette references): Skrine SFZ Incentives
- MIDA – Johor-Singapore Special Economic Zone (JS-SEZ) incentive information: MIDA JS-SEZ Incentives
- PwC Malaysia – Taxavvy Issue 13/2025 (overview of SFO scheme conditions): PwC Taxavvy 13/2025
Explore ways to safeguard your family's financial future with a complimentary 30-minute consultation (worth RM500)
Discover strategic wealth planning solutions tailored to your family’s needs with our complimentary consultation on trust structuring. We understand that every family has unique financial goals and challenges, requiring personalized approaches to long-term asset protection.
During your consultation, our experts will explore suitable trust structures aligned with your objectives, ensuring a smooth transition of wealth for future generations.
Schedule your free consultation today to gain insights into effective wealth preservation and legacy planning
Related Insights
Forest City SFO vs Labuan Trust vs Offshore Trust (2026)
Compare Forest City SFO (0% tax), Labuan trusts and offshore trusts. See AUM, substance, costs, layering strategies and best fit for Malaysians in 2026.
Family Office in Malaysia: 6 Major Reasons You Must Know Now
Family Office in Malaysia: Why You Must Know This Now (2026 Outlook) Last updated: 19 Feb 2026 Family Office Malaysia Forest City SFZ Family Office Incentive Scheme
Estate Planning in Malaysia: Will vs Trust vs Family Office
Importance of Estate Planning in Malaysia (2026): Will vs Trust vs Family Office Estate Planning Malaysia Will (Wasiat) Privat
The Truth About Labuan Family Offices: Is It Really an SFO?
Setup a Labuan Family Office in 2026. Compare Private Fund vs Waqf structures, understand requirements, and see the new FSA fee revisions.